DataFirst
Understanding the Relation between Noise and Bias
in Annotated Datasets
Motivation
- Bias in Annotation: Annotator differences in subjective tasks introduce bias in their annotations, especially in sensitive domains like hate speech recognition, stemming from diverse backgrounds and perspectives.
- Misinterpretation of Bias as Noise: Minority votes are often considered outliers by models. This causes models to perceive them as noise, leading to biased predictions favoring majority vote.
- In this project, we’ll explore if perspectivist classification models effectively utilize valuable insights from instances labeled as noisy by noise-detection techniques.
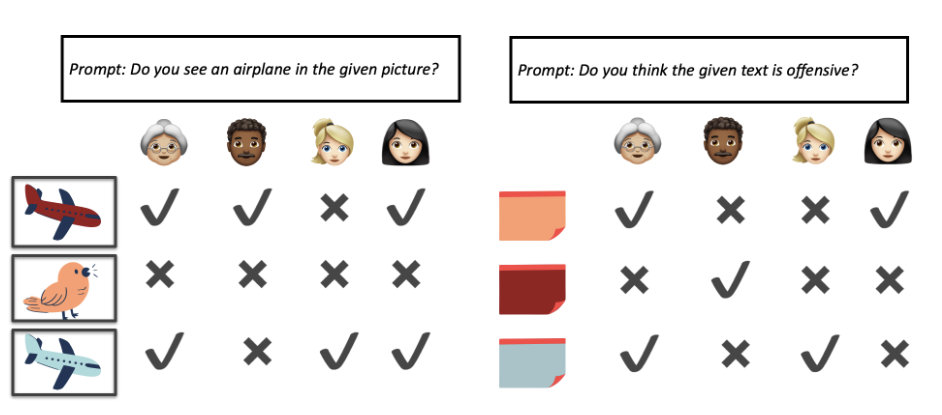
Problem Statement
In the evolving landscape of machine learning, the reliability and fairness of models hinge on the quality of annotated data. However, the presence of bias, particularly in subjective tasks, has become a critical concern. This is especially prominent in sensitive domains like hate speech recognition, where annotators, stemming from diverse backgrounds and perspectives, might introduce bias in their annotations.
Datasets
| Toxicity and Hate Speech | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SBIC [1] | Kennedy [2] | Agree to Disagree [3] | |
| # Annotators | 307 | 7,912 | 819 |
| # Annotations per annotator | 479±829.6 | 17.1±3.8 | 63.7±139 |
| # Unique texts | 45318 | 39,565 | 10,440 |
| # Annotations per text | 3.2±1.2 | 2.3±1.0 | 5 |
| # Labels | 2 | 3 | 2 |
Methodology
Two Regimes of Classification


MODEL AND PERFORMANCE
Model
Trained 2 models for each dataset
| Majority Label Model | Multi Annotator Model |
| Model - Roberta-Base [6] Epochs - 5 Learning Rate - 5e-5 Batch Size - 32 |
Model - DISCO [7] Epochs - 5 Learning Rate - 2e-3 Batch Size - 200 |
Performance
| Dataset | F1 Score (majority) | F1 Score (multi-annotator) |
| Agree to Disagree | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| Kennedy | 0.68 | 0.75 |
| SBIC | 0.80 | 0.78 |
Uncertainty in Machine Learning Predictions
- Data Cartography summarizes training dynamics for all samples as:
- Confidence: Mean of probabilities for gold label across epochs.
- Variability: Standard Deviation of probabilities for gold label across epochs.
Results
DATASET CARTOGRAPHY
AGREE TO DISAGREE

KENNEDY

SBIC

SINGLE GROUND TRUTH MODEL
AGREE TO DISAGREE

KENNEDY

SBIC

MULTI ANNOTATOR MODEL
AGREE TO DISAGREE

![group count]](plots_agree_to_disagree/group_count.png)
SBIC


KENNEDY


Analysis
High Confidence in Majority model and Low Confidence in Multi-Annotator model
Mislabeled annotations:
| Text | Annotation |
| I thought you were going to win this in a landslide | Offensive |
| crossing my fingers for you from Germany. Even though I am not an American. | Offensive |
| boy F**K you | Not Offensive |
| Fragility at its finest | Offensive |
Findings
Single Ground Truth Model
- There is correlation between human disagreement on instances and model’s uncertainty/confidence for classifying that instance.
- For instances that there is more disagreement among human labelers there is also low confidence from the single-GT model.
Multi-Annotator Model
- Like single gold label model, we see significant correlation between agreement between annotators and model confidence in all the datasets, with the confidence decreasing with more disagreement between the annotators.
- For low confidence samples in single ground truth model, we observe multi-annotator model having high confidence for labels which disagree with majority, hence learning valuable information from samples that majority vote aggregation discards.
- We see high number of annotations per annotator is necessary to model different perspectives effectively.
References
[1] Social Bias Frames: Reasoning about Social and Power Implications of Language (Sap et al., ACL 2020)
[2] Constructing interval variables via faceted Rasch measurement and multitask deep learning: a hate speech application (Kennedy et al., 2020)
[3] Agreeing to Disagree: Annotating Offensive Language Datasets with Annotators’ Disagreement (Leonardelli et al., EMNLP 2021)
[4] SemEval-2018 Task 1: Affect in Tweets (Mohammad et al., SemEval 2018)
[5] Dataset Cartography: Mapping and Diagnosing Datasets with Training Dynamics (Swayamdipta et al., EMNLP 2020)
[6] RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach (Yinhan Liu et al., 2019)
[7] Disagreement Matters: Preserving Label Diversity by Jointly Modeling Item and Annotator Label Distributions with DisCo (Weerasooriya et al., Findings 2023)
[8] Annotators with Attitudes: How Annotator Beliefs And Identities Bias Toxic Language Detection (Sap et al., NAACL 2022)
[9] Dealing with Disagreements: Looking Beyond the Majority Vote in Subjective Annotations (Mostafazadeh Davani et al., TACL 2022)
About the Team
|
Abhishek Anand
MS in Computer Science |
Anweasha Saha
MS in Computer Science |
Prathyusha Naresh Kumar
MS in Computer Science |
Negar Mokhberian
PhD in Computer Science |
Ashwin Rao
PhD in Computer Science |
Zihao He
PhD in Computer Science |





